Bitumen is used for road construction, roofing, waterproofing, and industrial protection. It acts as a binding and sealing agent, providing durability, water resistance, and flexibility. Bitumen is also used in soundproofing, damp-proofing, and protective coatings for metals and pipelines, making it essential in construction and infrastructure projects.
Bitumen is one of the most versatile and widely used materials in modern construction and infrastructure. From road surfacing to waterproofing, its unique properties make it an essential component across various industries. But what exactly is bitumen, and what is it used for? Whether you’re in construction, engineering, or simply curious about how this black, sticky substance shapes the world around us, this guide will explain everything you need to know, including what bitumen is made of, how it’s produced, and why it plays such a crucial role in daily life.
Understanding What Bitumen Is
Bitumen, often referred to as asphalt in some regions, is a viscous, black, or dark brown material derived from crude oil. It’s essentially the heavy residue left after the lighter hydrocarbons (like petrol and diesel) have been distilled off during the refining process. Naturally occurring bitumen can also be found in tar pits and oil sands.
To put it simply, bitumen acts as a binding and waterproofing agent, making it ideal for applications that require strength, durability, and resistance to water. Its sticky nature allows it to hold materials like aggregates together, forming tough and long-lasting surfaces.
What Is Bitumen Made Of?
When people ask, “What is bitumen made of?” the answer lies in its complex chemical composition. Bitumen is primarily composed of hydrocarbons, which are compounds made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms. These hydrocarbons are combined with small amounts of sulphur, nitrogen, oxygen, and trace metals.
There are four main chemical groups in bitumen:
- Asphaltenes: Responsible for their hardness and black colour.
- Resins: Provide adhesive and elastic properties.
- Aromatics: Offer flexibility and viscosity balance.
- Saturates: Contribute to smooth flow and temperature stability.
This unique combination of elements gives bitumen its flexibility under heat, water resistance, and impressive binding strength, qualities that make it indispensable in construction and engineering.
Types of Bitumen
Before exploring what bitumen is used for, it’s helpful to understand the different types available:
- Penetration Grade Bitumen: Commonly used for road surfacing, classified by its hardness and penetration value.
- Cutback Bitumen: Mixed with solvents to make it more fluid for cold-weather use or easier application.
- Emulsion Bitumen: Bitumen dispersed in water, used in road maintenance and surface dressing.
- Polymer-Modified Bitumen (PMB): Enhanced with polymers to improve elasticity and temperature resistance.
- Oxidised Bitumen: Treated with air to increase stiffness and resistance to heat, commonly used in roofing and waterproofing.
Each type is tailored for specific environments and applications, ensuring optimal performance in various conditions.
What Is Bitumen Used For?
Bitumen has an extensive range of uses, primarily because of its adhesive, waterproofing, and weather-resistant properties. Below are the main applications across industries:
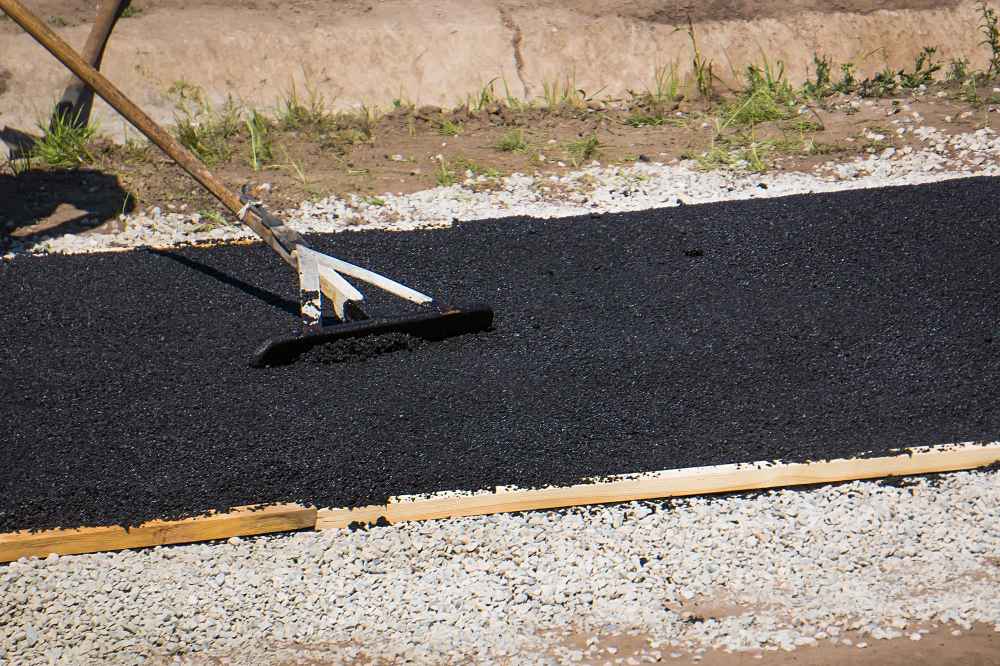
Road Construction
The most common and significant use of bitumen is in road construction. Around 85–90% of the world’s bitumen production goes into road paving.
When combined with aggregates such as crushed stone or sand, bitumen forms asphalt concrete, the smooth, durable surface we drive on daily. Its flexibility allows roads to withstand temperature changes, traffic pressure, and weather conditions.
Key Benefits in Road Building:
- Excellent water resistance, preventing potholes and erosion
- High durability and flexibility under heavy loads
- Smooth driving surface with reduced noise
- Cost-effective maintenance and repair
Different grades of bitumen are used depending on the type of road and climate. For instance, polymer-modified bitumen performs better in areas with extreme temperatures due to its enhanced elasticity.

Roofing and Waterproofing
Bitumen’s waterproofing properties make it an ideal material for roofing applications. It’s commonly used in bituminous membranes, roof felts, and torch-on roofing systems.
The material acts as a protective barrier against rain, snow, and moisture, ensuring roofs remain durable for years. Bitumen-based roofing products also resist UV rays and temperature fluctuations, which is vital for long-lasting roof protection.
Common Bitumen Roofing Applications:
- Flat or low-slope roofs
- Industrial building roofs
- Residential waterproof membranes
- Roof repair coatings
Damp Proofing
Bitumen is widely used as a damp-proof course (DPC) in construction to prevent rising damp in walls and floors. The substance is applied as a liquid coating or sheet membrane, creating a waterproof barrier that stops moisture from seeping upward through the structure.
This application is particularly common in older buildings or areas with high groundwater levels.
Soundproofing and Vibration Damping
Bitumen is also an effective soundproofing and vibration-damping material, often used in vehicle manufacturing and construction. Its dense composition helps reduce vibrations and absorb noise, making interiors quieter and more comfortable.
You’ll find bituminous sheets or mats applied beneath car floors, inside doors, and around engine compartments to reduce road and engine noise.
Industrial Coatings
In industrial applications, bitumen serves as a protective coating for metals, pipelines, and machinery. Its resistance to moisture and corrosion makes it ideal for coating steel structures, preventing rust and chemical damage.
For example, steel bridges, oil tanks, and water pipes are often coated with bituminous paint or emulsion to extend their lifespan and enhance performance in harsh environments.
Airport Runways and Pavements
Bitumen’s durability and resilience make it suitable for airport runways, taxiways, and pavements. These areas endure intense pressure from aircraft landings and temperature changes, so bitumen-based asphalt is used for its flexibility, strength, and ability to resist deformation.
Railway Tracks and Platforms
Bitumen also finds applications in railway track construction and station platforms, where it serves as a binder in track ballast and provides waterproof surfaces that reduce maintenance costs.
Bitumen in Waterproof Paints and Sealants
Bitumen is commonly found in waterproof paints, mastics, and sealants used in both residential and commercial projects. When applied to concrete, metal, or wood, it forms a protective film that prevents water infiltration and surface degradation.
It’s especially useful in:
- Basements and foundations
- Bridges and tunnels
- Storage tanks
- Water channels and gutters
Roofing Felt and Shingles
Bituminous roofing felt is a popular material used under roof tiles and shingles as an additional layer of protection. It helps extend the lifespan of the roof by keeping water out and reducing heat loss.
Road Maintenance and Repair
Bitumen plays a major role in pothole repair and surface sealing. Bitumen emulsions and cold-mix asphalt products make it easier to patch up roads quickly and efficiently without requiring full resurfacing.
These maintenance solutions are cost-effective, durable, and applicable in varying weather conditions, ensuring safer roads all year round.
Environmental Aspects of Bitumen
While bitumen is derived from crude oil, modern production methods and recycling initiatives have made it more sustainable than ever. Bitumen used in road construction can be recycled multiple times without losing its key properties. Reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) is now widely reused in new road surfaces, reducing waste and the need for fresh raw materials.
Additionally, the use of low-temperature bitumen mixes has helped lower carbon emissions during road construction, contributing to more eco-friendly practices across the industry.
Bitumen vs. Tar: What’s the Difference?
People often confuse bitumen with tar, but they are not the same. Bitumen is a by-product of petroleum refining, whereas tar is produced from coal. Bitumen is less toxic, more stable, and far more commonly used in construction today.
Storage and Handling of Bitumen
Bitumen must be stored at controlled temperatures to maintain its workability. It’s typically kept in heated tanks and transported in insulated tankers. Safety is essential when handling bitumen, as it can cause burns if mishandled while hot.
Future Developments in Bitumen Technology
The future of bitumen lies in innovation and sustainability. Researchers are developing bio-based and synthetic alternatives to traditional petroleum bitumen. These eco-friendly variants aim to reduce dependency on fossil fuels while maintaining performance standards.
Additionally, smart roads, which incorporate self-healing or temperature-sensitive bitumen, are currently being explored to make infrastructure more durable and energy-efficient.
Bitumen and 123 Oil
Trusted suppliers like 123 Oil play a vital role in delivering high-quality bitumen products across industries. Their refined bitumen grades are used in construction, roofing, and road surfacing, ensuring strength, longevity, and performance under varying weather conditions.
Summary: Why Bitumen Remains Indispensable
So, what is bitumen used for? The answer spans across multiple industries: it’s a binder, waterproofing agent, protective coating, and soundproofing material, all rolled into one. Its ability to withstand extreme weather, resist water, and bond firmly with aggregates makes it one of the most reliable construction materials in the world.
From smooth roads and durable roofs to waterproof basements and quiet vehicles, bitumen continues to shape modern infrastructure and urban development. Understanding what bitumen is made of and its various applications helps us appreciate just how integral this remarkable material is to everyday life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bitumen is primarily made of hydrocarbons derived from crude oil, along with small amounts of sulphur, nitrogen, oxygen, and trace metals.
Bitumen is mainly used in road construction, roofing, waterproofing, industrial coatings, and soundproofing applications.
While bitumen is a petroleum product, it can be recycled and reused, reducing waste and environmental impact. Modern production methods also lower carbon emissions.
Bitumen is the binding component, while asphalt is the mixture of bitumen and aggregates used to create road surfaces.
Yes. Reclaimed asphalt containing bitumen can be reheated and reused in new road projects without losing performance quality.